public class FIRST {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("WELCOME TO JAVA");
}
}
==========================================
public class SECOND {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Asha\n Asha Bhavan\n Pothencode \n Trivandrum");
}
}
================================================
public class THIRD {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println(" 1\n 1\t2\n 1\t2\t3\n 1\t2\t3\t4 \n 1\t2\t3\t4\t5 ");
}
}
=================================================
public class fourth {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("\t\t*\n\t*\t\t*\n*\t\t*\t\t*");
}
}
============================================================
public class calculation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int a=2;//variable declaratn
int b=4;
int c=a+b;
int d=a-b;
int e=a*b;
int f=a/b;
//System.out.println("sum="+c);
//System.out.println("difference="+d);
//System.out.println("multiplication="+e);
//System.out.println("division="+f);
System.out.println("sum="+c+ "\ndifference="+d+ "\nproduct="+e+ "\ndivision="+f);
}
}
===================================================================
public class areasquare {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int a=3;
int c=a*a;
System.out.println("area of square="+c);
}
}
==============================================================
public class areasquare {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int a=3;
int c=a*a;
System.out.println("area of square="+c);
}
}
=============================================================
public class operator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int x=10;
System.out.println(x++);
System.out.println(++x);
System.out.println(x--);
System.out.println(--x);
int a=8;
int b=10;
System.out.println(a++ + ++a);//8+10=18
System.out.println(b++ + b++);//10+11=21
} }
============================================================
public class unary {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int a=22;
int b=-25;
boolean c=true;
boolean d=false;
System.out.println(~a);
System.out.println(~b);
System.out.println(!c);
System.out.println(!d);
}}
======================================================================
public class modulus {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int a=9;
int b=3;
int c=a%b;
System.out.println(c);
}}
=======================================================================
public class logical {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int a=6;
int b=2;
int c=8;
System.out.println(a<b||a<c);
System.out.println(a<b&a<c);
}}
===============================================================
public class logical {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int a=6;
int b=2;
int c=8;
System.out.println(a<b||a<c);
System.out.println(a<b&a<c);
}}
===============================================================
public class assignment {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int a=10;
int b=20;
a*=4;
b/=2;
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
}}
====================================================================
public class ifff {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int age=20;
if(age>18) {
System.out.print("age is greater than 18");
}}}
================================================================
public class vote {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int age=80;
if (age>=18)
{
System.out.println("Eligible for vote");
}
else
{
System.out.println("Not eligible for vote");
)}}
==============================================================
public class positive {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int a=0;
if (a>=0)
{
System.out.println("It is a positive number");
}
else
{
System.out.println("It is a negative number");
}}}
====================================================================
public class big {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int a=10;
int b=8;
if(a<b)
{
System.out.println("a is the smallest number");
}
else
{
System.out.println("b is the smallest number");
}}}
===============================================================
import java.util.Scanner;
public class odd {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("enter a number");
int x=input.nextInt();
if(x%2==0)
{
System.out.println("It is an even number");
}
else {
System.out.println("It is an odd number");
}}}
==================================================================
Exception Handling in Java
What is Exception in JavaDictionary Meaning: Exception is an abnormal condition.In Java, an exception is an event that disrupts the normal flow of the program. It is an object which is thrown at runtime. Advantage of Exception HandlingThe core advantage of exception handling is to maintain the normal flow of the application. An exception normally disrupts the normal flow of the application that is why we use exception handling. Let's take a scenario: Suppose there are 10 statements in your program and there occurs an exception at statement 5, the rest of the code will not be executed i.e. statement 6 to 10 will not be executed. If we perform exception handling, the rest of the statement will be executed. That is why we use exception handling in Java. 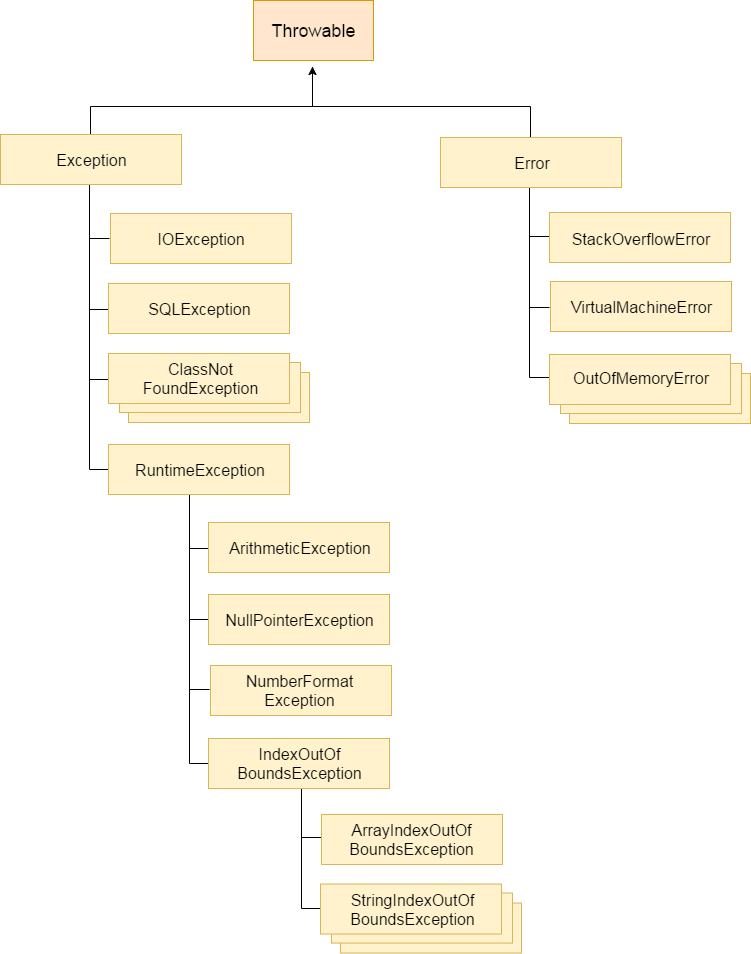 Types of Java ExceptionsThere are mainly two types of exceptions: checked and unchecked. Here, an error is considered as the unchecked exception. According to Oracle, there are three types of exceptions:
 Difference between Checked and Unchecked Exceptions1) Checked ExceptionThe classes which directly inherit Throwable class except RuntimeException and Error are known as checked exceptions e.g. IOException, SQLException etc. Checked exceptions are checked at compile-time. 2) Unchecked ExceptionThe classes which inherit RuntimeException are known as unchecked exceptions e.g. ArithmeticException, NullPointerException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException etc. Unchecked exceptions are not checked at compile-time, but they are checked at runtime. 3) ErrorError is irrecoverable e.g. OutOfMemoryError, VirtualMachineError, AssertionError etc. Java Exception KeywordsThere are 5 keywords which are used in handling exceptions in Java.
|
- import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
- import java.io.PrintWriter;
- public class TryCatchExample10 {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- PrintWriter pw;
- try {
- pw = new PrintWriter("jtp.txt"); //may throw exception
- pw.println("saved");
- }
- // providing the checked exception handler
- catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
- System.out.println(e);
- }
- System.out.println("File saved successfully");
- }
- }


No comments:
Post a Comment