Windows
Application(Desktop application)
Software
Development
Front end :
c#.net
Backend : SQL
Server
Project 1
using System;
using
System.Collections.Generic;
using
System.ComponentModel;
using
System.Data; using
System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using
System.ComponentModel;
using
System.Data;
using
System.Drawing;
using
System.Linq;
using
System.Text;
using
System.Threading.Tasks;
using
System.Windows.Forms;
namespace _2
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show("Welcome
" + textBox1.Text);
}
}
}
]
using
System.Drawing;
using
System.Linq;
using
System.Text;
using
System.Threading.Tasks;
using
System.Windows.Forms;
namespace
project1
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show("Good
Morning");
}
}
}
Sum
namespace WindowsFormsApp3
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
int a =
Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
int b =
Convert.ToInt32(textBox2.Text);
int c = a + b;
MessageBox.Show(c.ToString());
}
}
}
Product of three
numbers
namespace
WindowsFormsApp3
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
int a =
Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
int b =
Convert.ToInt32(textBox2.Text);
int c =
Convert.ToInt32(textBox3.Text);
int d = a * b * c;
MessageBox.Show("Product
="+d.ToString());
}
Product
display inside the window
namespace
WindowsFormsApp3
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
int a =
Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
int b =
Convert.ToInt32(textBox2.Text);
int c =
Convert.ToInt32(textBox3.Text);
int d = a * b * c;
textBox4.Text=("Product
="+d.ToString());
}
Calculator
public partial
class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
int a = Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
int b = Convert.ToInt32(textBox2.Text);
int c = a+ b;
int d = a-b;
int z = a * b;
int f = a / b;
textBox3.Text = c.ToString();
textBox4.Text = d.ToString();
textBox5.Text = z.ToString();
textBox6.Text = f.ToString();
}
}
private void button1_Click(object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
int a =
Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
if (a % 2 == 0)
{
textBox2.Text =
"Even";
}
else
{
textBox2.Text =
"Odd";
}
; }
}
Biggest of two
numbers
private void
button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
int a = Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
int b = Convert.ToInt32(textBox2.Text);
if (a > b)
{
textBox3.Text = a.ToString();
}
else
{
textBox3.Text = b.ToString();
}
}
Calculator
public
calculator()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void
button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
int a = Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
int b = Convert.ToInt32(textBox2.Text);
int c = a+ b;
textBox3.Text = c.ToString();
}
private void
button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
int a = Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
int b = Convert.ToInt32(textBox2.Text);
int c = a - b;
textBox3.Text = c.ToString();
}
private void
button3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
int a = Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
int b = Convert.ToInt32(textBox2.Text);
int c = a * b;
textBox3.Text = c.ToString();
}
private void
button4_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
int a = Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
int b = Convert.ToInt32(textBox2.Text);
int c = a / b;
textBox3.Text = c.ToString();
}
While loop
public partial
class listboxeg : Form
{
public listboxeg()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
int i = 0;
while (i <= 10)
{
listBox1.Items.Add(i);
i++;
}
=========================================
public
listboxeg2cs()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void
button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
listBox1.Items.Add("Devi");
listBox1.Items.Add("Devu");
listBox1.Items.Add("Dev");
listBox1.Items.Add("Devika");
listBox1.Items.Add("Devan");
listBox1.Items.Add("Devilk");
Combo Box
public partial class combobox1 : Form
{
public combobox1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show("You selected
: " + comboBox2.Text);
}
}
Radio button
private void
button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
String Gender = "";
if (radioButton1.Checked == true)
{
Gender = radioButton1.Text;
}
else if (radioButton2.Checked == true)
{
Gender = radioButton2.Text;
}
MessageBox.Show("You are " +
Gender.ToString());
}
Tree View
private void treeView1_AfterSelect(object
sender, TreeViewEventArgs e)
{
TreeNode node = treeView1.SelectedNode;
MessageBox.Show(String.Format("you
selected:{0}", node.Text));
}
private void Treeview_Load(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
TreeNode = new
TreeNode("Windows");
treeView1.Nodes.Add(treenode);
treenode = new
TreeNode("Linux");
treeView1.Nodes.Add(treenode);
TreeNode node2 = new
TreeNode("C#");
TreeNode node3 = new
TreeNode("vb.net");
TreeNode[] array = new TreeNode[] {
node2, node3 };
treenode = new TreeNode("dotnet
pearls", array);
treeView1.Nodes.Add(treenode);
}
}
Collections
Stack(LIFO-Last in First out)
Push – Inserting an element
into the stack is known as push
Pop – Deleting an element from
a stack is known as pop
public partial
class Form1 : Form
{
Stack s = new Stack();
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void textBox1_TextChanged(object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
s.Push(textBox1.Text);
MessageBox.Show("pushed");
}
private void button2_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
listBox1.Items.Add(s.Pop());
}
}
Queue(FIFO-First in first out)
Enqueue-Inserting
an element into the queue is known as enqueue
Dequeue-Deleting
an element from the queue is known as dequeue
public partial
class Queueeg : Form
{
Queue q = new Queue();
public Queueeg()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
q.Enqueue(textBox1.Text);
MessageBox.Show("Enqued");
}
private void button2_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
listBox1.Items.Add(q.Dequeue());
}
Globalisation
public partial
class globalization : Form
{
public globalization()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
CultureInfo[] cul =
CultureInfo.GetCultures(CultureTypes.SpecificCultures);
foreach (CultureInfo c in cul)
{
listBox1.Items.Add(c.DisplayName);
}
}
}
Domain updown
private void domain_updown_Load(object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
DomainUpDown.DomainUpDownItemCollection
items = this.domainUpDown1.Items;
items.Add("sql");
items.Add("java");
items.Add("pearl");
items.Add(".net");
this.domainUpDown1.Text =
"dot";
}
private void
domainUpDown1_SelectedItemChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.Text = domainUpDown1.Text;
}
Notify icon
public notifications()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
notifyIcon1.BalloonTipText =
"today is vaentine day";
notifyIcon1.BalloonTipTitle =
"remember";
notifyIcon1.ShowBalloonTip(0);
}
Properties
Notify
icon properties -àAppearences-àBallonTipIconàcan chose below three
option it will change the appearance of the footer pop up window
·
Info
·
Warning
·
Error
Checked list box
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
for (int i = 0; i <
checkedListBox1.Items.Count; i++)
{
if (checkedListBox1.GetItemChecked(i))
{
checkedListBox2.Items.Add(checkedListBox1.Items[i].ToString());
}
}
private void button2_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
for (int i = 0; i <
checkedListBox2.Items.Count; i++)
{
if (checkedListBox2.GetItemChecked(i))
{
checkedListBox2.Items.Remove(checkedListBox2.Items[i].ToString());
}
}
Datetime Picker
public Datetimepicker()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void
dateTimePicker1_ValueChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
label1.Text =
dateTimePicker1.Value.ToString();
}
}
File System
Watcher
private void
fileSystemWatcher1_Changed(object sender, System.IO.FileSystemEventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show(String.Format("changed:{0}{1}", e.FullPath,
e.ChangeType));
}
private void
fileSystemWatcher1_Created(object sender, System.IO.FileSystemEventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show(String.Format("created:{0}{1}", e.FullPath,
e.ChangeType));
}
private void
fileSystemWatcher1_Deleted(object sender, System.IO.FileSystemEventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show(String.Format("deleted:{0}{1}", e.FullPath,
e.ChangeType));
}
private void
fileSystemWatcher1_Renamed(object sender, System.IO.RenamedEventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show(String.Format("renamed:{0}{1}", e.FullPath,
e.ChangeType));
}
}
·
Need to set path in properties
·
Run the prgm
·
Message box will appear displaying the actions
performed in that particular folder
File
Operations
public
fileoperations()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private
void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
FileStream fs = new
FileStream(@"C:\Users\devik\Desktop\CSS//sample.txt",
FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write);
StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(fs);
sw.Write(textBox1.Text);
sw.Flush();
sw.Close();
}
private
void button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
textBox1.Clear();
}
private
void button3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
FileStream fs = new
FileStream(@"C:\Users\devik\Desktop\CSS//sample.txt", FileMode.Open,
FileAccess.Read);
StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(fs);
textBox1.Text = sr.ReadToEnd();
sr.Close();
}
Calculator
public
partial class calculator : Form
{
double FirstNumber;
string Operation;
public calculator()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button17_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
textBox1.Clear();
}
private void button18_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
Application.Exit();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
if (textBox1.Text == "0"
&& textBox1.Text != null)
{
textBox1.Text = "1";
}
else
{
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text +
"1";
}
}
private void button2_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
if (textBox1.Text == "0"
&& textBox1.Text != null)
{
textBox1.Text = "2";
}
else
{
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text +
"2";
}
}
private void button3_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
if (textBox1.Text == "0"
&& textBox1.Text != null)
{
textBox1.Text = "3";
}
else
{
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text +
"3";
}
}
private void button4_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
if (textBox1.Text == "0"
&& textBox1.Text != null)
{
textBox1.Text = "4";
}
else
{
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text +
"4";
}
}
private void button5_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
if (textBox1.Text == "0"
&& textBox1.Text != null)
{
textBox1.Text = "5";
}
else
{
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text +
"5";
}
}
private void button6_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
if (textBox1.Text == "0"
&& textBox1.Text != null)
{
textBox1.Text = "6";
}
else
{
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text +
"6";
}
}
private void button7_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
if (textBox1.Text == "0"
&& textBox1.Text != null)
{
textBox1.Text = "7";
}
else
{
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text +
"7";
}
}
private void button8_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
if (textBox1.Text == "0"
&& textBox1.Text != null)
{
textBox1.Text = "8";
}
else
{
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text +
"8";
}
}
private void button9_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
if (textBox1.Text == "0"
&& textBox1.Text != null)
{
textBox1.Text = "9";
}
else
{
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text +
"9";
}
}
private void button10_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text +
"0";
}
private void button11_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
FirstNumber =
Convert.ToDouble(textBox1.Text);
textBox1.Text = "0";
Operation = "+";
}
private void button12_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
FirstNumber =
Convert.ToDouble(textBox1.Text);
textBox1.Text = "0";
Operation = "-";
}
private void button13_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
FirstNumber =
Convert.ToDouble(textBox1.Text);
textBox1.Text = "0";
Operation = "*";
}
private void button14_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
FirstNumber =
Convert.ToDouble(textBox1.Text);
textBox1.Text = "0";
Operation = "/";
}
private void button19_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
FirstNumber =
Convert.ToDouble(textBox1.Text);
textBox1.Text = "0";
Operation = "%";
}
private void button20_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
textBox1.Text = "0";
}
private void button15_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text +
".";
}
private void button16_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
double SecondNumber;
double Result;
SecondNumber =
Convert.ToDouble(textBox1.Text);
if (Operation == "+")
{
Result = (FirstNumber +
SecondNumber);
textBox1.Text =
Convert.ToString(Result);
FirstNumber = Result;
}
if (Operation == "-")
{
Result = (FirstNumber -
SecondNumber);
textBox1.Text =
Convert.ToString(Result);
FirstNumber = Result;
}
if (Operation == "*")
{
Result = (FirstNumber *
SecondNumber);
textBox1.Text =
Convert.ToString(Result);
FirstNumber = Result;
}
if (Operation == "/")
{
Result = (FirstNumber /
SecondNumber);
textBox1.Text =
Convert.ToString(Result);
FirstNumber = Result;
}
if (Operation == "%")
{
Result = (FirstNumber %
SecondNumber);
textBox1.Text =
Convert.ToString(Result);
FirstNumber = Result;
}
NotePad
namespace
collection
{
public partial class notepad : Form
{
public notepad()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void
newToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
richTextBox1.Clear();
}
private void
openToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
openFileDialog1.ShowDialog();
string fName =
openFileDialog1.FileName;
StreamReader sr = new
StreamReader(fName);
richTextBox1.Text = sr.ReadToEnd();
sr.Close();
}
private void
saveToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
saveFileDialog1.ShowDialog();
string fName =
saveFileDialog1.FileName;
StreamWriter sw = new
StreamWriter(fName);
sw.Write(richTextBox1.Text);
sw.Flush();
sw.Close();
}
private void
saveAsToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
saveFileDialog1.ShowDialog();
string fName =
saveFileDialog1.FileName;
StreamWriter sw = new
StreamWriter(fName);
sw.Write(richTextBox1.Text);
sw.Flush();
sw.Close();
}
private void
printToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
printDialog1.ShowDialog();
}
private void
closeToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Application.Exit();
}
private void
undoToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
richTextBox1.Undo();
}
private void
redoToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
richTextBox1.Redo();
}
private void
cutToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
richTextBox1.Cut();
}
private void
copyToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
richTextBox1.Copy();
}
private void
pasteToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
richTextBox1.Paste();
}
private void
fontToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
fontDialog1.ShowDialog();
richTextBox1.Font =
fontDialog1.Font;
}
private void
colourToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (colorDialog1.ShowDialog() ==
DialogResult.OK)
{
richTextBox1.ForeColor =
colorDialog1.Color;
}
}
private void
pageSetupToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
pageSetupDialog1.Document =
printDocument1;
pageSetupDialog1.ShowDialog();
}
private void
aboutToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Form f = new Form();
TextBox ll = new TextBox();
ll.Text = "MICROSOFT SOFTWARE
LICENSE TERMS WINDOWS 7 ULTIMATE SERVICE PACK 1 These license terms are an
agreement between Microsoft Corporation (or based on where you live, one of its
affiliates) and you. Please read them. They apply to the software named above,
which includes the media on which you received it, if any. Printed-paper
license terms, which may come with the software, may replace or modify any
on-screen license terms.";
ll.Font
= new Font("Arial", 8);
ll.Dock = DockStyle.Fill;
f.Controls.Add(ll);
f.Show();
}
private void
statusBarToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
label1.Text =
"Cols"+richTextBox1.Text.Length;
}
private void
wordWrapToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (richTextBox1.WordWrap == false)
richTextBox1.WordWrap =
wordWrapToolStripMenuItem.Checked;
}
}
}
Exception
Handling
Exception
Handling in C#:-An exception is defined as an event that occurs during the
execution of a program that is unexpected by the program code. The actions to
be performed in case of occurrence of an exception is not known to the program.
In such a case, we create an exception object and call the exception handler
code. The execution of an exception handler so that the program code does not
crash is called exception handling. Exception handling is important because it
gracefully handles
an
unwanted event, an exception so that the program code still makes sense to the
user.
Syntax:
try
{
//
statements that may cause an exception
}
catch(
Exception obj)
{
//
handler code
}
Keywords
for exception handling
Divide
by zero
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
try
{
int a =
Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
int b =
Convert.ToInt32(textBox2.Text);
int c = a / b;
label3.Text = c.ToString();
}
catch (DivideByZeroException ex)
{
// Handle divide by zero exception
MessageBox.Show("Error: Cannot
divide by zero.", "Divide By Zero Error", MessageBoxButtons.OK,
MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
catch (FormatException ex)
{
// Handle invalid input format
MessageBox.Show("Error: Please
enter valid numbers.", "Input Error", MessageBoxButtons.OK,
MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
}
}
Array Index out of Bound Exception
Design
Outputs
public partial class arrayindex_outofbound
: Form
{
public arrayindex_outofbound()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
try
{
// Initialize an array of 5
integers
int[] numbers = new int[5] {
10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
// Get the index from the
TextBox
int index =
int.Parse(textBox1.Text);
// Attempt to access the array
element at the specified index
int result = numbers[index];
label1.Text = "Element at
index " + index + " is: " + result.ToString();
}
catch (IndexOutOfRangeException ex)
{
// Handle
IndexOutOfRangeException if the index is invalid
MessageBox.Show("Error:
Index out of range. Please enter a valid index between 0 and 4.",
"Index Out of Range Error", MessageBoxButtons.OK,
MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
catch (FormatException ex)
{
// Handle invalid input format
(e.g., non-integer input)
MessageBox.Show("Error:
Please enter a valid integer index.", "Input Error",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{ // Catch any other exceptions\r\n
MessageBox.Show("An
unexpected error occurred: " + ex.Message, "Error",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
}
SDI
– Single Document Interface
MDI
– Multiple Document Interface
Form
Linking
private void button2_Click(object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
arrayindex_outofbound obj1 = new
arrayindex_outofbound();
obj1.Show();
}
MDI
– Multiple Document Interface
New
prgms àform
rename parent -à
Properties àIS
MDI container àTrue
Design
Menu
script à
File àRed
green blue
Arrange à
Tile cascade
Format
àColour
Code
public
partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void
redToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
FRMred red = new FRMred();
red.MdiParent = this;
red.Show();
}
private void
greenToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
FRMGreen green= new FRMGreen();
green.MdiParent = this;
green.Show();
}
private void
blueToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
FRMblue blue = new FRMblue();
blue.MdiParent = this;
blue.Show();
}
private void
tileToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.LayoutMdi(MdiLayout.TileHorizontal);
}
private void
cascadeToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.LayoutMdi(MdiLayout.TileVertical);
}
private void
colourToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (colorDialog1.ShowDialog() ==
DialogResult.OK)
this.ActiveMdiChild.BackColor =
colorDialog1.Color;
}
}
ADO.net --- Active data object
.network enabling technology
What
is ADO.NET?
ADO
stands for Microsoft ActiveX Data Objects. ADO.NET is one of Microsoft’s data
access technologies, which we can use to communicate with different data
sources. It is a part of the .NET Framework, which connects the .NET
Application (Console, WCF, WPF, Windows, MVC, Web Form, etc.) and different
data sources. The Data Sources can be SQL Server, Oracle, MySQL, XML, etc.
ADO.NET consists of a set of predefined classes that can be used to connect,
retrieve, insert, update, and delete data (i.e., performing CRUD operation)
from data sources.
What
Types of Applications Use ADO.NET?
ADO.NET is used in various applications where
data access and manipulation are crucial. Here are some types of applications
that commonly use ADO.NET:
Desktop
Applications: Traditional desktop applications like Windows Forms and WPF
applications often need to interact with databases or other data sources.
ADO.NET provides the necessary tools to connect to databases, retrieve data,
and update records.
Web
Applications: Web applications, including ASP.NET Web Forms and ASP.NET MVC
applications, require data access to display, collect, and manage information.
ADO.NET enables these applications to connect to databases and present data to
users.
Console
Applications: Console applications might need to perform data-related
tasks, like importing/exporting data, data analysis, or reporting. ADO.NET can
facilitate these tasks by providing efficient data access.
Service
Applications: Background or Windows services that process data often rely
on ADO.NET to connect to databases and handle data-related operations.
Components of ADO.NET
Components
are designed for data manipulation and faster data access. Connection, Command,
DataReader, DataAdapter, DataSet, and DataView are the components of ADO.NET
that are used to perform database operations. ADO.NET comprises several key
components that work together to facilitate data access and manipulation in
.NET applications. These components provide the building blocks for connecting
to data sources, executing queries, retrieving and updating data, and managing
transactions.
Here
are the main components of ADO.NET:
Connection:
The Connection component establishes a connection to a data source, such as a
database. It manages the underlying connection to the database server and
provides methods to open and close the connection.
Command:
The Command component represents a command that is executed against a data
source. It encapsulates SQL statements, stored procedure calls, and other
database commands. The two main types of command objects are SQLCommand, which
is used for executing SQL queries and stored procedures against SQL Server
databases, and OleDbCommand, which is Used for executing commands against OLE
DB data sources, which include various database types.
DataReader:
The DataReader component efficiently reads data from a data source. It provides
a forward-only, read-only stream of data that is particularly useful for
retrieving large datasets. Reading data with a DataReader is fast and
memory-efficient.
DataAdapter:
The DataAdapter bridges the application’s DataSet (in-memory cache of data) and
the data source. It facilitates the retrieval of data from the data source into
the DataSet and also allows changes to be updated in the DataSet back to the
data source. Specific DataAdapter classes exist for different data sources,
such as SqlDataAdapter and OleDbDataAdapter.
DataSet:
The DataSet is an in-memory data cache that can hold multiple tables,
relationships, and constraints. It allows disconnected data manipulation,
meaning that data is retrieved from the data source, disconnected from the
connection, and then manipulated without direct interaction with the data
source. The Data Set can be considered an in-memory representation of the
database.
DataTable:
A data table is a component within a Data Set that represents a table of data.
It consists of rows and columns and allows you to store and manipulate tabular
data. Data Tables can have relationships and constraints to maintain data
integrity.
Data
View: The Data View is used to filter, sort, and navigate through data
within a Data Table. It provides a dynamic view of the data, allowing you to
customize how it is presented to the user.
Transaction:
The Transaction component provides support for managing transactions in
ADO.NET. Transactions group multiple data access operations into a single unit
of work that can be either committed (made permanent) or rolled back (undone)
as a whole.
Connection
String: The connection string is a configuration string that provides
the necessary information to connect to a data source. It includes details such
as the database server’s location, credentials, and other settings.
ADO.NET
has two main components that are used for accessing and manipulating data. They
are as follows: Data Provider and Dataset.
Remember
that the ADO.NET objects (Connection, Command, Data Reader, and Data Adapter)
have different prefixes depending on the provider, as shown below.
Connection
– SQL Connection, Oracle Connection, OleDbConnection, OdbcConnection, etc.
Command – SQL Command, Oracle Command, OleDbCommand, OdbcCommand, etc. Data
Reader – SQLDataReader, OracleDataReader, OleDbDataReader, OdbcDataReader, etc.
DataAdapter – SQLDataAdapter, OracleDataAdapter, OleDbDataAdapter,
OdbcDataAdapter, etc.
Data
GridView Binding
From
Tool box select àData
Grid View àChose
data sources
Using
code
using
System;
using
System.Collections.Generic;
using
System.ComponentModel;
using
System.Data;
using
System.Drawing;
using
System.Linq;
using
System.Text;
using
System.Threading.Tasks;
using
System.Windows.Forms;
using
System.Data.SqlClient;
using
System.Configuration;
namespace
gridviewbinding
{
public partial class Form3 : Form
{
SqlConnection con = new
SqlConnection(@"Data Source=DESKTOP-9DL12AG\SQLEXPRESS;Initial Catalog=dbcollege;Integrated
Security=True;");
public Form3()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
con.Open();
SqlCommand cmd = new
SqlCommand("select * from tblemployee",con);
SqlDataAdapter adp = new
SqlDataAdapter(cmd);
DataSet ds = new DataSet();
adp.Fill(ds);
dataGridView1.DataSource = ds;
dataGridView1.DataMember =
ds.Tables[0].ToString();
con.Close();
}
}
}
using
System;
using
System.Collections.Generic;
using
System.ComponentModel;
using
System.Data;
using
System.Drawing;
using
System.Linq;
using
System.Text;
using
System.Threading.Tasks;
using
System.Windows.Forms;
using
System.Data.SqlClient;
using
System.Configuration;
using
static System.Windows.Forms.VisualStyles.VisualStyleElement;
namespace
gridviewbinding
{
public partial class Form5 : Form
{
SqlConnection con = new
SqlConnection(@"Data Source=DESKTOP-9DL12AG\SQLEXPRESS;Initial
Catalog=dbtechmatrix;Integrated Security=True;");
public Form5()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
con.Open();
SqlCommand cmd = new
SqlCommand("insert into tblstudent values
('"+textBox1.Text+"','"+textBox2.Text+"','"+textBox3.Text+"','"+comboBox1.Text+"','"+comboBox2.Text+"','"+textBox4.Text+"')",con);
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
con.Close();
MessageBox.Show("Inserted
successfully");
}
private void button2_Click(object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
con.Open();
SqlCommand cmd = new
SqlCommand("select * from tblstudent", con);
SqlDataAdapter adp = new
SqlDataAdapter(cmd);
DataSet ds = new DataSet();
adp.Fill(ds);
dataGridView1.DataSource = ds;
dataGridView1.DataMember =
ds.Tables[0].ToString();
con.Close();
}
private void Form5_Load(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
con.Open();
SqlCommand cmd = new
SqlCommand("select id from tblstudent", con);
SqlDataAdapter adp = new
SqlDataAdapter( cmd);
DataTable dt = new DataTable();
adp.Fill(dt);
comboBox3.DataSource = dt;
comboBox3.DisplayMember =
"id";
comboBox3.ValueMember =
"id";
con.Close();
}
private void button3_Click(object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
con.Open();
SqlCommand cmd = new
SqlCommand("select * from tblstudent where id='" +
Convert.ToInt32(comboBox3.SelectedValue) + "'", con);
SqlDataAdapter adp = new
SqlDataAdapter(cmd);
DataSet ds = new DataSet();
adp.Fill(ds);
dataGridView1.DataSource = ds;
dataGridView1.DataMember =
ds.Tables[0].ToString();
SqlDataReader rd =
cmd.ExecuteReader();
while (rd.Read())
{
textBox1.Text =
rd.GetString(1);
textBox2.Text =
rd.GetInt32(2).ToString();
textBox3.Text =
rd.GetString(3);
comboBox1.Text =
rd.GetString(4);
comboBox2.Text =
rd.GetString(5);
textBox4.Text =
rd.GetInt32(6).ToString();
}
con.Close();
}
private void button4_Click(object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
con.Open();
SqlCommand cmd = new
SqlCommand("update tblstudent set studentname='" + textBox1.Text +
"',age='" + Convert.ToInt32(textBox2.Text) + "',city='" +
textBox3.Text + "',course='" + comboBox1.Text + "',mode='"
+ comboBox2.Text + "',fees='"+Convert.ToInt32(textBox4.Text)+"'
where id='" + comboBox3.SelectedValue + "'",con);
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
con.Close();
}
private void button5_Click(object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
con.Open();
SqlCommand cmd = new
SqlCommand("delete from tblstudent where id='" +
comboBox3.SelectedValue + "'", con);
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
con.Close();
}
}
}
Windows
Application
1. Message
Box
private void
button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show("welcome "
+textBox1.Text);
}
2. Calculation
private void
button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
int
a=Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
int b =
Convert.ToInt32(textBox2.Text);
int c =
a + b;
textBox3.Text=c.ToString();
int d =
a - b;
textBox4.Text=d.ToString();
int f =
a * b;
textBox5.Text=f.ToString();
int g =
a / b;
textBox6.Text=g.ToString();
}
3. ComboBox
private void
comboBox1_SelectedIndexChanged(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
label2.Text = comboBox1.SelectedItem.ToString();
}
private void
Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
comboBox1.Items.Add("AI");
comboBox1.Items.Add("HTML");
comboBox1.Items.Add("CSS");
}
4.
private void
button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
int a = Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
int b = Convert.ToInt32(textBox2.Text);
int c = a + b;
textBox3.Text = c.ToString();
}
private void
button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
int a =
Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
int b =
Convert.ToInt32(textBox2.Text);
int d =
a - b;
textBox3.Text = d.ToString();
}
private void
button3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
int a =
Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
int b =
Convert.ToInt32(textBox2.Text);
int f =
a * b;
textBox3.Text = f.ToString();
}
private void
button4_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
int a =
Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
int b =
Convert.ToInt32(textBox2.Text);
int g =
a / b;
textBox3.Text = g.ToString();
}
}
5.
private void
comboBox1_SelectedIndexChanged(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
int
a=Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
int b =
Convert.ToInt32(textBox2.Text);
int c;
if
(comboBox1.SelectedIndex == 0)
{
c
= a + b;
textBox3.Text = c.ToString();
}
else if
(comboBox1.SelectedIndex == 1)
{
c
= a - b;
textBox3.Text = c.ToString();
}
else if
(comboBox1.SelectedIndex == 2)
{
c
= a * b;
textBox3.Text = c.ToString();
}
else if
(comboBox1.SelectedIndex == 3)
{
c
= a / b;
textBox3.Text = c.ToString();
}
else
textBox3.Text = "INVALID";
}
6.List Box
{
listBox1.Items.Add("C#");
listBox1.Items.Add("ASP");
listBox1.Items.Add("JAVA");
listBox1.Items.Add("PYTHON");
}
7.
namespace WindowsFormsApp4
{
internal static class Program
{
/// <summary>
/// The
main entry point for the application.
/// </summary>
[STAThread]
static void
Main()
{
Application.EnableVisualStyles();
Application.SetCompatibleTextRenderingDefault(false);
Application.Run(new secondform());
}
}
}
private void
button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Form1
form = new Form1();
this.Hide();
form.Show();
}
private void
button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Form1
form = new Form1();
this.Hide();
form.Show();
}
8. Color Dialog
public partial class thirdform :
Form
{
public thirdform()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void
button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if(colorDialog1.ShowDialog()
== DialogResult.OK)
{
this.BackColor
= colorDialog1.Color;
}
}
}
}
9.
if(colorDialog1.ShowDialog()
== DialogResult.OK)
{
this.BackColor
= colorDialog1.Color;
button1.BackColor = colorDialog1.Color;
}
10. Radio
Button
private void
button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
int a =
Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
int b =
Convert.ToInt32(textBox2.Text);
int c;
if(radioButton1.Checked
==true)
{
c =
a + b;
textBox3.Text=c.ToString();
}
else if
(radioButton2.Checked == true)
{
c =
a - b;
textBox3.Text = c.ToString();
}
else if
(radioButton3.Checked == true)
{
c =
a * b;
textBox3.Text = c.ToString();
}
else if
(radioButton4.Checked == true)
{
c =
a / b;
textBox3.Text = c.ToString();
}
}
11. TreeView
Eg1:
private void
treeView1_AfterSelect(object sender,
TreeViewEventArgs e)
{
TreeNode node = treeView1.SelectedNode;
MessageBox.Show(String.Format("you selected:{0}",
node.Text));
}
private void
TreeView_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
TreeNode treenode = new TreeNode("Windows");
treeView1.Nodes.Add(treenode);
treenode = new TreeNode("Linux");
treeView1.Nodes.Add(treenode);
TreeNode node2 = new TreeNode("C#");
TreeNode node3 = new TreeNode("vb.net");
TreeNode[] array = new TreeNode[] {
node2, node3 };
treenode
= new TreeNode("dotnet pearls",
array);
treeView1.Nodes.Add(treenode);
}
}
Eg2:
private void
Form2_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
TreeNode
tree = new TreeNode("SQL");
treeView1.Nodes.Add(tree);
tree = new TreeNode("PYTON");
treeView1.Nodes.Add(tree);
TreeNode
tree1 = new TreeNode("ASP.NET");
TreeNode
tree2 = new TreeNode("VB.NET");
TreeNode[] array1 = new TreeNode[] {
tree1, tree2 };
tree = new
TreeNode(".NET", array1);
treeView1.Nodes.Add(tree);
}
private void
treeView1_AfterSelect(object sender,
TreeViewEventArgs e)
{
TreeNode
node = treeView1.SelectedNode;
textBox1.Text= node.Text;
//MessageBox.Show(String.Format("you
selected:{0}", node.Text));
}
12. Stack [Last In First Out]
using System.Collections;
public partial class Stackexample :
Form
{
Stack
s=new Stack();
public Stackexample()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void
button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
s.Push(textBox1.Text);
MessageBox.Show("pushed");
}
private void
button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
listBox1.Items.Add(s.Pop());
}
13. Queue
[First In First Out]
using System.Collections;
namespace WindowsFormsApp4
{
public partial class QueueExample :
Form
{
Queue q = new Queue();
public QueueExample()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void
button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
q.Enqueue(textBox1.Text);
MessageBox.Show("Enqueue");
}
14. Menu Strip
private void
queueToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
QueueExample
queueExample = new QueueExample();
queueExample.Show();
}
private void
stackToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
Stackexample stackexample = new
Stackexample();
stackexample.Show();
}
private void
treeViewToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
TreeView treeView = new TreeView();
treeView.Show();
}
private void
radioButtonToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
RadioButton radioButton = new RadioButton();
radioButton.Show();
}
private void
undoToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
richTextBox1.Undo();
}
private void
redoToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
richTextBox1.Redo();
}
private void
cutToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
richTextBox1.Cut();
}
private void
copyToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
richTextBox1.Copy();
}
private void
pasteToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs
e)
{
richTextBox1.Paste();
}
private void
selectAllToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
richTextBox1.SelectAll();
}
private void
dateTimeToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
richTextBox1.Text = DateTime.Now.ToString();
}
private void
closeToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
Application.Exit();
}
private void
newToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
richTextBox1.Clear();
}
private void
foreColorToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
if(colorDialog1.ShowDialog()
== DialogResult.OK)
{
richTextBox1.ForeColor = colorDialog1.Color;
}
}
private void backColorToolStripMenuItem_Click(object
sender, EventArgs e)
{
if(colorDialog1.ShowDialog()==DialogResult.OK)
{
richTextBox1.BackColor=colorDialog1.Color;
}
}
15.
Font Dialog
private void
fontToolStripMenuItem1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
if(fontDialog1.ShowDialog()==DialogResult.OK
)
{
richTextBox1.Font = fontDialog1.Font;
}
}
1. IsmdiCondainer property=true
2. Form border style
property=none
3. RadioButton rb = new RadioButton();
rb.MdiParent= this;
rb.Show();
=====================================
Windows Application(Desktop application) Software Development
Front
end : c#.net Backend : SQL Server
Project
1
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic; using
System.ComponentModel; using System.Data; using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using
System.ComponentModel; using System.Data;
using System.Drawing; using System.Linq; using
System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks; using
System.Windows.Forms;
namespace _2
{
public partial
class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show("Welcome "
+ textBox1.Text);
}
}
}
]
using System.Drawing; using System.Linq; using
System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks; using
System.Windows.Forms;
namespace project1
{
public partial
class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
}
Sum
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show("Good
Morning");
}
}
namespace WindowsFormsApp3
{
public partial
class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
int a = Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
int b = Convert.ToInt32(textBox2.Text);
int c = a + b; MessageBox.Show(c.ToString());
}
}
}
Product
of three numbers namespace WindowsFormsApp3
{
public partial
class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
int a = Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
int b = Convert.ToInt32(textBox2.Text);
int c = Convert.ToInt32(textBox3.Text);
int d = a * b * c;
MessageBox.Show("Product
="+d.ToString());
}
Product display inside
the window
namespace WindowsFormsApp3
{
public partial
class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
int a = Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
int b = Convert.ToInt32(textBox2.Text);
int c = Convert.ToInt32(textBox3.Text);
int d = a * b * c;
textBox4.Text=("Product ="+d.ToString());
}
Calculator
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
int a = Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
int b = Convert.ToInt32(textBox2.Text);
int c = a+ b; int d = a-b; int
z = a * b; int f = a / b;
textBox3.Text
= c.ToString(); textBox4.Text = d.ToString();
textBox5.Text = z.ToString(); textBox6.Text = f.ToString();
}
}
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
int a = Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
if (a % 2 == 0)
{
}
else
{
}
; }
}
textBox2.Text = "Even";
textBox2.Text = "Odd";
Biggest of two numbers
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
int a = Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
int b = Convert.ToInt32(textBox2.Text);
if (a > b)
{
textBox3.Text = a.ToString();
}
else
{
textBox3.Text = b.ToString();
}
}
Calculator
public calculator()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
int a = Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
int b = Convert.ToInt32(textBox2.Text);
int c = a+ b;
textBox3.Text = c.ToString();
}
private void button2_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
int a = Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
int b = Convert.ToInt32(textBox2.Text);
int c = a - b;
textBox3.Text = c.ToString();
}
private void button3_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
int a = Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
int b = Convert.ToInt32(textBox2.Text);
int c = a * b;
textBox3.Text = c.ToString();
}
private void button4_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
int a = Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
int b = Convert.ToInt32(textBox2.Text);
int c = a / b;
textBox3.Text = c.ToString();
}
While loop
public partial class listboxeg
: Form
{
public listboxeg()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
int i = 0;
while (i <=
10)
{
listBox1.Items.Add(i); i++;
}
=========================================
public listboxeg2cs()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
listBox1.Items.Add("Devi");
listBox1.Items.Add("Devu"); listBox1.Items.Add("Dev");
listBox1.Items.Add("Devika"); listBox1.Items.Add("Devan");
listBox1.Items.Add("Devilk");
Combo Box
public partial
class combobox1 : Form
{
public combobox1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show("You selected
: " + comboBox2.Text);
}
}
Radio button
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
String Gender
= "";
if
(radioButton1.Checked == true)
{
Gender = radioButton1.Text;
}
else if
(radioButton2.Checked == true)
{
Gender = radioButton2.Text;
}
MessageBox.Show("You are " + Gender.ToString());
}
Tree View
private void treeView1_AfterSelect(object sender,
TreeViewEventArgs e)
{
TreeNode node = treeView1.SelectedNode;
MessageBox.Show(String.Format("you selected:{0}", node.Text));
}
private void Treeview_Load(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
TreeNode treenode
= new TreeNode("Windows");
treeView1.Nodes.Add(treenode);
treenode = new TreeNode("Linux");
treeView1.Nodes.Add(treenode);
TreeNode node2 = new
TreeNode("C#");
TreeNode node3 = new
TreeNode("vb.net");
TreeNode[] array = new TreeNode[] { node2, node3 };
treenode = new TreeNode("dotnet pearls", array);
treeView1.Nodes.Add(treenode);
}
}
Collections
Stack(LIFO-Last in First out)
Push – Inserting an element into the stack is known as push Pop – Deleting an
element from a stack is known as pop public partial class Form1 : Form
{
Stack s = new Stack(); public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void textBox1_TextChanged(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
}
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
s.Push(textBox1.Text);
MessageBox.Show("pushed");
}
private void button2_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
listBox1.Items.Add(s.Pop());
}
}
Queue(FIFO-First in first out)
Enqueue-Inserting
an element into the queue is known as enqueue Dequeue-Deleting an element from the queue
is known as dequeue
public partial class Queueeg : Form
{
Queue q = new Queue();
public Queueeg()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
q.Enqueue(textBox1.Text);
MessageBox.Show("Enqued");
}
private void button2_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
listBox1.Items.Add(q.Dequeue());
}
Globalisation
public partial class
globalization : Form
{
public globalization()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
CultureInfo[] cul = CultureInfo.GetCultures(CultureTypes.SpecificCultures);
foreach (CultureInfo c in cul)
{
listBox1.Items.Add(c.DisplayName);
}
}
}
Domain updown
private void domain_updown_Load(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
DomainUpDown.DomainUpDownItemCollection items = this.domainUpDown1.Items; items.Add("sql");
items.Add("java");
items.Add("pearl");
items.Add(".net"); this.domainUpDown1.Text = "dot";
}
private void domainUpDown1_SelectedItemChanged(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
this.Text = domainUpDown1.Text;
}
Notify icon
public notifications()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
notifyIcon1.BalloonTipText = "today is vaentine day"; notifyIcon1.BalloonTipTitle =
"remember"; notifyIcon1.ShowBalloonTip(0);
}
Properties
Notify icon properties -àAppearences-àBallonTipIconàcan chose below three option it will change the appearance of the footer pop up
window
·
Info
·
Warning
·
Error
Checked list box
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
for (int i =
0; i < checkedListBox1.Items.Count; i++)
{
if (checkedListBox1.GetItemChecked(i))
{
checkedListBox2.Items.Add(checkedListBox1.Items[i].ToString());
}
}
private void button2_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
for (int i =
0; i < checkedListBox2.Items.Count; i++)
{
if (checkedListBox2.GetItemChecked(i))
{
checkedListBox2.Items.Remove(checkedListBox2.Items[i].ToString());
}
}
Datetime Picker
public Datetimepicker()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void dateTimePicker1_ValueChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
label1.Text = dateTimePicker1.Value.ToString();
}
}
File System Watcher
private void fileSystemWatcher1_Changed(object sender, System.IO.FileSystemEventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show(String.Format("changed:{0}{1}", e.FullPath, e.ChangeType));
}
private void fileSystemWatcher1_Created(object sender, System.IO.FileSystemEventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show(String.Format("created:{0}{1}", e.FullPath, e.ChangeType));
}
private void fileSystemWatcher1_Deleted(object sender, System.IO.FileSystemEventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show(String.Format("deleted:{0}{1}", e.FullPath, e.ChangeType));
}
private void fileSystemWatcher1_Renamed(object sender, System.IO.RenamedEventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show(String.Format("renamed:{0}{1}", e.FullPath, e.ChangeType));
}
}
·
Need
to set path in properties
·
Run
the prgm
· Message box will appear displaying the actions performed in that particular folder
//path set in the watcher
properties,the create new folder in that folder inside and rename delete also
its show the message box.its watched that path folder
File
Operations public fileoperations()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
//write into the file,the
textbox details write into the file
FileStream fs = new FileStream(@"C:\Users\devik\Desktop\CSS//sample.txt", FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write);
StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(fs); sw.Write(textBox1.Text);
sw.Flush();
sw.Close();
}
private void button2_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
textBox1.Clear();
}
private void button3_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
//read from file,the content
of file show in textbox
FileStream fs = new FileStream(@"C:\Users\devik\Desktop\CSS//sample.txt", FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(fs); textBox1.Text =
sr.ReadToEnd(); sr.Close();
}
Calculator
public partial
class calculator : Form
{
double FirstNumber;
string Operation; public calculator()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button17_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
textBox1.Clear();
}
private void button18_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
Application.Exit();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
if
(textBox1.Text == "0" && textBox1.Text != null)
{
textBox1.Text = "1";
}
else
{
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text + "1";
}
}
private void button2_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
if
(textBox1.Text == "0" && textBox1.Text != null)
{
textBox1.Text = "2";
}
else
{
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text + "2";
}
}
private void button3_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
if (textBox1.Text == "0" && textBox1.Text != null)
{
textBox1.Text = "3";
}
else
{
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text + "3";
}
}
private void button4_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
if
(textBox1.Text == "0" && textBox1.Text != null)
{
textBox1.Text = "4";
}
else
{
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text + "4";
}
}
private void button5_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
if
(textBox1.Text == "0" && textBox1.Text != null)
{
textBox1.Text = "5";
}
else
{
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text + "5";
}
}
private void button6_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
if (textBox1.Text == "0" && textBox1.Text != null)
{
textBox1.Text = "6";
}
else
{
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text + "6";
}
}
private void button7_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
if
(textBox1.Text == "0" && textBox1.Text != null)
{
textBox1.Text = "7";
}
else
{
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text + "7";
}
}
private void button8_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
if
(textBox1.Text == "0" && textBox1.Text != null)
{
textBox1.Text = "8";
}
else
{
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text + "8";
}
}
private void button9_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
if (textBox1.Text == "0" && textBox1.Text != null)
{
textBox1.Text = "9";
}
else
{
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text + "9";
}
}
private void button10_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text + "0";
}
private void button11_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
FirstNumber =
Convert.ToDouble(textBox1.Text); textBox1.Text
= "0";
Operation = "+";
}
private void button12_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
FirstNumber =
Convert.ToDouble(textBox1.Text); textBox1.Text
= "0";
Operation = "-";
}
private void button13_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
FirstNumber =
Convert.ToDouble(textBox1.Text); textBox1.Text
= "0";
Operation = "*";
}
private void button14_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
FirstNumber =
Convert.ToDouble(textBox1.Text); textBox1.Text
= "0";
Operation = "/";
}
private void button19_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
FirstNumber =
Convert.ToDouble(textBox1.Text); textBox1.Text
= "0";
Operation = "%";
}
private void button20_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
textBox1.Text = "0";
}
private void button15_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
textBox1.Text = textBox1.Text + ".";
}
private void button16_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
double SecondNumber;
double Result;
SecondNumber = Convert.ToDouble(textBox1.Text);
if (Operation == "+")
{
Result = (FirstNumber + SecondNumber); textBox1.Text = Convert.ToString(Result); FirstNumber
= Result;
}
if
(Operation == "-")
{
Result = (FirstNumber - SecondNumber); textBox1.Text = Convert.ToString(Result); FirstNumber
= Result;
}
if (Operation == "*")
{
Result = (FirstNumber * SecondNumber); textBox1.Text = Convert.ToString(Result); FirstNumber
= Result;
}
if (Operation == "/")
{
Result = (FirstNumber / SecondNumber); textBox1.Text = Convert.ToString(Result); FirstNumber
= Result;
}
if (Operation == "%")
{
Result = (FirstNumber % SecondNumber); textBox1.Text = Convert.ToString(Result); FirstNumber
= Result;
}
NotePad
namespace collection
{
public partial class
notepad : Form
{
public notepad()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void newToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
richTextBox1.Clear();
}
private void openToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
openFileDialog1.ShowDialog();
string fName = openFileDialog1.FileName;
StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(fName);
richTextBox1.Text = sr.ReadToEnd();
sr.Close();
}
private void saveToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
saveFileDialog1.ShowDialog();
string fName = saveFileDialog1.FileName;
StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(fName);
sw.Write(richTextBox1.Text);
sw.Flush();
sw.Close();
}
private void saveAsToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
saveFileDialog1.ShowDialog();
string fName = saveFileDialog1.FileName;
StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(fName);
sw.Write(richTextBox1.Text);
sw.Flush();
sw.Close();
}
private void printToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
printDialog1.ShowDialog();
}
private void closeToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Application.Exit();
}
private void undoToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
richTextBox1.Undo();
}
private void redoToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
richTextBox1.Redo();
}
private void cutToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
richTextBox1.Cut();
}
private void copyToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
richTextBox1.Copy();
}
private void pasteToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
richTextBox1.Paste();
}
private void fontToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
fontDialog1.ShowDialog();
richTextBox1.Font = fontDialog1.Font;
}
private void colourToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (colorDialog1.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
richTextBox1.ForeColor = colorDialog1.Color;
}
}
private void pageSetupToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
pageSetupDialog1.Document = printDocument1;
pageSetupDialog1.ShowDialog();
}
private void aboutToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Form f = new Form(); TextBox ll = new TextBox();
WARE LICENSE TERMS WINDOWS
7 ULTIMATE SERVICE
PACK 1 These license
terms are an agreement between Microsoft
Corporation (or based on where you live, one of its affiliates) and you. Please
read them. They apply to the software named above, which includes the media on
which you received it, if any. Printed-paper license terms, which may come with the software, may replace or modify any on-screen license
terms.";
ll.Font = new Font("Arial", 8);
ll.Dock = DockStyle.Fill; f.Controls.Add(ll);
f.Show();
}
private void statusBarToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
label1.Text = "Cols"+richTextBox1.Text.Length;
}
private void wordWrapToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (richTextBox1.WordWrap == false)
richTextBox1.WordWrap = wordWrapToolStripMenuItem.Checked;
}
}
}
Added
1)
Richbox
2)
Menustrip
3)
Openfiledialogue
4)
Savefiledialogue
5)
Colordialogue
6)
Printdialogue
7)
Pagesetupdialogue
8)
Printdocument
9)
Fontdialogue
10)
![]()
Status strip 11) label
Exception Handling
Exception Handling in C#:-An exception is
defined as an event that occurs during the execution of a program that is
unexpected by the program code. The actions to be performed in case of occurrence of an exception is not known
to the program. In such a
case, we create an exception object
and call the exception handler
code. The execution of an
exception handler so that the program
code does not crash is called
exception handling. Exception handling is important because it gracefully
handles
an unwanted event, an exception so that the program code still
makes sense to the user.
Syntax:
try
{
// statements that may cause an exception
}
catch( Exception obj)
{
// handler code
}
Keywords for exception handling
Divide by zero
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
try
{
int a = Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text); int b = Convert.ToInt32(textBox2.Text); int c = a
/ b;
label3.Text = c.ToString();
}
catch (DivideByZeroException ex)
{
// Handle divide by zero exception
MessageBox.Show("Error: Cannot divide by zero.", "Divide By Zero Error", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
catch (FormatException ex)
{
// Handle invalid
input format
MessageBox.Show("Error: Please enter valid numbers.", "Input Error", MessageBoxButtons.OK,
MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
}
}
Design
![]()
Outputs
Array Index out of Bound
Exception
Design
![]()
Output in exception
Output without
exception
![]()
public partial
class arrayindex_outofbound : Form
{
public arrayindex_outofbound()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
try
{
// Initialize
an array of 5 integers
int[] numbers
= new int[5] { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
// Get the index from the TextBox int index = int.Parse(textBox1.Text);
// Attempt to access the array element
at the specified index int
result = numbers[index];
label1.Text = "Element at index " + index + " is: " + result.ToString();
}
catch
(IndexOutOfRangeException ex)
{
//
Handle IndexOutOfRangeException if the index is invalid
MessageBox.Show("Error: Index out of range. Please
enter a
valid index between 0 and 4.", "Index Out of Range Error",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
catch
(FormatException ex)
{
// Handle
invalid input format (e.g., non-integer input) MessageBox.Show("Error: Please enter a valid integer
index.",
"Input Error",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
catch
(Exception ex)
{ //
Catch any other exceptions\r\n
MessageBox.Show("An unexpected error occurred: " + ex.Message, "Error",
MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
}
SDI – Single
Document Interface
The above documents are single document
interfaces because the projects
only one form or document only
MDI – Multiple
Document Interface
Form Linking
private void button2_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
arrayindex_outofbound obj1 = new arrayindex_outofbound(); obj1.Show();
}
MDI – Multiple Document Interface
The form select
-> Properties ->IS
MDI container set às True (parent form)
Design
Menu script->file (name
title)->sub Red, green,
blue Arrange ->Tile cascade
Format ->Colour
![]()
The next 3 forms set as blue ,green red are the back ground color example
The blue select blue form is show green ->green form red->redform
We select tile or cascade this arrange cascade or tile forms
We select the form and form->color then we have to change the
background color also show below
![]()
Select 3 forms Tle form below
Cascade
![]()
We change the color
Code
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void redToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
FRMred red = new FRMred(); red.MdiParent = this; red.Show();
}
private void greenToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
FRMGreen green= new FRMGreen();
green.MdiParent = this; green.Show();
}
private void blueToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
FRMblue blue = new FRMblue(); blue.MdiParent = this; blue.Show();
}
private void tileToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
this.LayoutMdi(MdiLayout.TileHorizontal);
}
private void cascadeToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
this.LayoutMdi(MdiLayout.TileVertical);
}
private void colourToolStripMenuItem_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
if (colorDialog1.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
this.ActiveMdiChild.BackColor = colorDialog1.Color;
}
}
Example
Add new form in project right
click solution Add ->new fidwos
form ->name ->ok First doc
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic; using
System.ComponentModel; using System.Data;
using System.Drawing; using System.Linq; using
System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks; using
System.Windows.Forms;
namespace WindowsFormsApplication3
{
public partial
class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
try
{
int a = Convert.ToInt32(textBox1.Text);
int b = Convert.ToInt32(textBox2.Text);
int c = a / b;
labelResult.Text = c.ToString();
}
catch (DivideByZeroException ex)
{
// Handle divide by zero exception
MessageBox.Show("Error:
Cannot divide by zero.", "Divide By Zero
Error", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
catch
(FormatException ex)
{
// Handle
invalid input format
MessageBox.Show("Error: Please enter valid numbers.", "Input Error", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
}
private void button2_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
try
{
// Initialize
an array of 5 integers
int[] numbers
= new int[5] { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
// Get the index from the TextBox int index = int.Parse(textBox3.Text);
// Attempt to access the array
element at the specified index
int result = numbers[index];
label3.Text = "Element at index "
+ index + " is: " + result.ToString();
}
catch
(IndexOutOfRangeException ex)
{
// Handle IndexOutOfRangeException if the index is invalid
MessageBox.Show("Error: Index out of range. Please enter a valid index
between 0
and 4.", "Index Out
of Range Error", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
catch
(FormatException ex)
{
// Handle
invalid input format (e.g., non-integer input)
MessageBox.Show("Error: Please enter a valid integer
index.", "Input Error", MessageBoxButtons.OK,
MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
catch
(Exception ex)
{ //
Catch any other exceptions\r\n
MessageBox.Show("An unexpected error occurred: " + ex.Message,
"Error", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
}
private void button3_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
Form2 obj = new Form2(); obj.Show();
}
}
}
Second doc using System;
using System.Collections.Generic; using
System.ComponentModel; using System.Data;
using System.Drawing; using System.Linq; using
System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks; using
System.Windows.Forms;
namespace WindowsFormsApplication3
{
public partial
class Form2 : Form
{
public Form2()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
Form1 obj = new Form1(); obj.Show();
}
}
}
This is the form2 window click button the page jump to first form vise versa.
ADO.net --- Active data object .network enabling technology
What is ADO.NET?
ADO stands for Microsoft ActiveX Data Objects.
ADO.NET is one of Microsoft’s data access technologies, which we can use to communicate with different data sources. It is a part of the .NET Framework, which
connects the .NET Application (Console, WCF, WPF, Windows, MVC, Web Form,
etc.) and different data sources. The Data Sources
can be SQL Server, Oracle, MySQL, XML, etc. ADO.NET consists of a set of
predefined classes that can be used to connect, retrieve, insert, update, and
delete data (i.e., performing CRUD operation) from data sources.
What Types of Applications Use ADO.NET?
ADO.NET is used in
various applications where data access and manipulation are crucial. Here are
some types of applications that commonly use ADO.NET:
Desktop
Applications: Traditional
desktop applications like Windows Forms and WPF applications often need to
interact with databases or other data sources. ADO.NET provides the necessary
tools to connect to databases, retrieve data, and update records.
Web Applications: Web applications, including ASP.NET Web Forms and
ASP.NET MVC applications, require data access to display, collect, and manage
information. ADO.NET enables these applications to connect to databases and
present data to users.
Console Applications: Console applications might need to perform data-related tasks, like
importing/exporting data, data analysis, or reporting. ADO.NET can facilitate these tasks
by providing efficient data access.
Service
Applications: Background or
Windows services that process data often rely on ADO.NET to connect to
databases and handle data-related operations.
Components of ADO.NET
Components are designed for data
manipulation and faster data access. Connection, Command, DataReader,
DataAdapter, DataSet, and DataView are the components of ADO.NET that are used
to perform database operations. ADO.NET comprises several key components that
work together to facilitate data access and manipulation in .NET applications.
These components provide the building blocks for connecting to data sources,
executing queries, retrieving and updating data, and managing
transactions.
Here are the main components of ADO.NET:
Connection: The Connection component establishes a connection to a
data source, such as a database. It manages the underlying connection to the
database server and provides methods to open and close the connection.
Command: The
Command component represents a command that is executed against a data source.
It encapsulates SQL statements, stored procedure calls, and other database
commands. The two main types of command
objects are SQLCommand, which is used for executing SQL queries and stored
procedures against SQL Server databases, and OleDbCommand, which is Used for
executing commands against OLE DB data sources, which include various database
types.
DataReader: The
DataReader component efficiently reads data from a data source. It provides a
forward-only, read-only stream of data that is particularly useful
for retrieving large
datasets. Reading data with a DataReader is fast and memory-efficient.
DataAdapter: The
DataAdapter bridges the application’s DataSet (in-memory cache of data) and the
data source. It facilitates the retrieval of data from the data source into the
DataSet and also allows changes to be updated in the DataSet back to the data
source. Specific DataAdapter classes exist for different data sources, such as SqlDataAdapter and OleDbDataAdapter.
DataSet: The
DataSet is an in-memory data cache that can hold multiple tables,
relationships, and constraints. It allows disconnected data manipulation,
meaning that data is retrieved from
the data source, disconnected from the connection, and then manipulated without
direct interaction with the data source. The Data Set can be considered an
in-memory representation of the database.
DataTable: A data
table is a component within a Data Set that represents a table of data.
It consists of rows and columns and allows you to store
and manipulate tabular
data. Data Tables can have
relationships and constraints to maintain data integrity.
Data View: The
Data View is used to filter,
sort, and navigate
through data within
a Data Table. It provides a
dynamic view of the data, allowing you to customize how it is presented to the
user.
Transaction: The
Transaction component provides support for managing transactions in ADO.NET.
Transactions group multiple data access operations into a single
unit of work that can be either committed (made
permanent) or rolled back (undone) as a whole.
Connection String: The
connection string is a configuration string that provides the necessary
information to connect to a data source. It includes details
such as the database
server’s location, credentials, and other settings.
ADO.NET has two main components that are used
for accessing and manipulating data. They are as follows: Data Provider and
Dataset.
Remember that the ADO.NET objects (Connection,
Command, Data Reader, and Data Adapter) have different prefixes depending on
the provider, as shown below.
Connection – SQL Connection,
Oracle Connection, OleDbConnection, OdbcConnection, etc. Command – SQL
Command, Oracle Command, OleDbCommand, OdbcCommand, etc. Data Reader –
SQLDataReader, OracleDataReader, OleDbDataReader, OdbcDataReader, etc.
DataAdapter – SQLDataAdapter, OracleDataAdapter, OleDbDataAdapter, OdbcDataAdapter,
etc.
![]()
DatagridView add
From Tool box select
àData Grid View àChose data sources
using MySql.Data.MySqlClient; using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel; using System.Data;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
using System.Drawing; using
System.Linq;
using
System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace WindowsFormsApplicationDB
{
public partial
class Form1 : Form
{
MySqlConnection con = new MySqlConnection("Server=localhost;Database=student;User
ID=root;Password=touchq;");
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
con.Open();
MySqlCommand cmd = new MySqlCommand("select * from student", con); MySqlDataAdapter adp = new MySqlDataAdapter(cmd);
DataSet ds = new DataSet();
adp.Fill(ds); dataGridView1.DataSource = ds;
dataGridView1.DataMember = ds.Tables[0].ToString();
con.Close();
}
}
}
The Connection Pgm
Form 1
using MySql.Data.MySqlClient; using System;
using System.Collections.Generic; using
System.ComponentModel; using System.Data;
using System.Data.SqlClient; using
System.Drawing; using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace WindowsFormsApplicationDB
{
public partial class
Form1 : Form
{
// SqlConnection con = new SqlConnection(@"Server=localhost;Database=student;User
ID=root;Password=touchq;");
MySqlConnection con = new MySqlConnection("Server=localhost;Database=student;User
ID=root;Password=touchq;");
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
con.Open();
MySqlCommand cmd = new MySqlCommand("select * from
student", con);
MySqlDataAdapter adp = new MySqlDataAdapter(cmd);
DataSet ds = new DataSet();
adp.Fill(ds); dataGridView1.DataSource = ds;
dataGridView1.DataMember = ds.Tables[0].ToString();
con.Close();
}
private void button2_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
FormInsert obj = new FormInsert();
obj.Show();
}
}
}
![]()
Design Datagridview and 2
Form Insert
using MySql.Data.MySqlClient; using System;
using System.Collections.Generic; using
System.ComponentModel; using System.Data;
using System.Drawing; using System.Linq; using
System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace WindowsFormsApplicationDB
{
public partial
class FormInsert : Form
{
MySqlConnection con = new MySqlConnection("Server=localhost;Database=student;User
ID=root;Password=touchq;");
public FormInsert()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button3_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
this.Close();
}
private void FormInsert_Load(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
con.Open();
MySqlCommand cmd = new MySqlCommand("select studentid from student", con);
MySqlDataAdapter adp = new MySqlDataAdapter(cmd);
DataTable dt = new DataTable();
adp.Fill(dt); comboBoxid.DataSource = dt;
comboBoxid.DisplayMember = "studentid";
comboBoxid.ValueMember = "studentid";
con.Close();
}
private void comboBoxid_SelectedIndexChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
private void button1_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
con.Open();
MySqlCommand cmd = new MySqlCommand("insert into student (`Name`,`batch`,`Mark`) values ('" + textBoxName.Text + "','" + textBoxbatch.Text + "','" +
textBoxmark.Text + "')", con);
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery(); con.Close();
MessageBox.Show("Inserted successfully");
}
private void button4_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
con.Open();
MySqlCommand cmd = new MySqlCommand("update student set Name='" +
textBoxName.Text + "',batch='" + textBoxbatch.Text+
"',Mark='" +Convert.ToDouble( textBoxmark.Text) + "' where
studentid='" + comboBoxid.SelectedValue + "'", con);
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
con.Close();
}
private void button2_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
con.Open();
MySqlCommand cmd = new MySqlCommand("delete from student where
studentid='" + comboBoxid.SelectedValue + "'", con);
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
con.Close();
}
private void button5_Click(object sender,
EventArgs e)
{
con.Open();
MySqlCommand cmd = new MySqlCommand("select * from
student where studentid='" + Convert.ToInt32(comboBoxid.SelectedValue) +
"'", con);
MySqlDataAdapter adp = new MySqlDataAdapter(cmd);
DataSet ds = new DataSet();
adp.Fill(ds);
Form1
obj = new Form1(); obj.dataGridView1.DataSource = ds;
obj.dataGridView1.DataMember = ds.Tables[0].ToString();
MySqlDataReader rd = cmd.ExecuteReader(); while (rd.Read())
{
textBoxName.Text
= rd.GetString(1); textBoxbatch.Text =
rd.GetString(2).ToString();
textBoxmark.Text = rd.GetString(3);
}
con.Close();
}
}
}
Design
![]()
Output
When we click show button
![]()
We click Next page
![]()
The combobox
student name load data. update ,delete and save buttons are done insert update delete from
the database





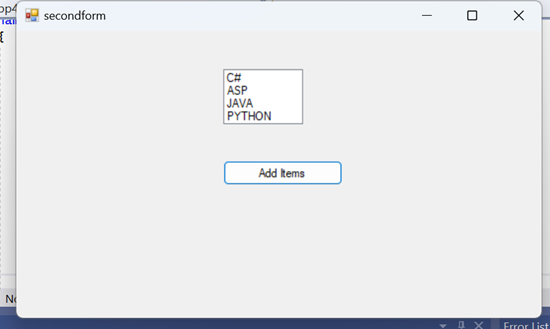



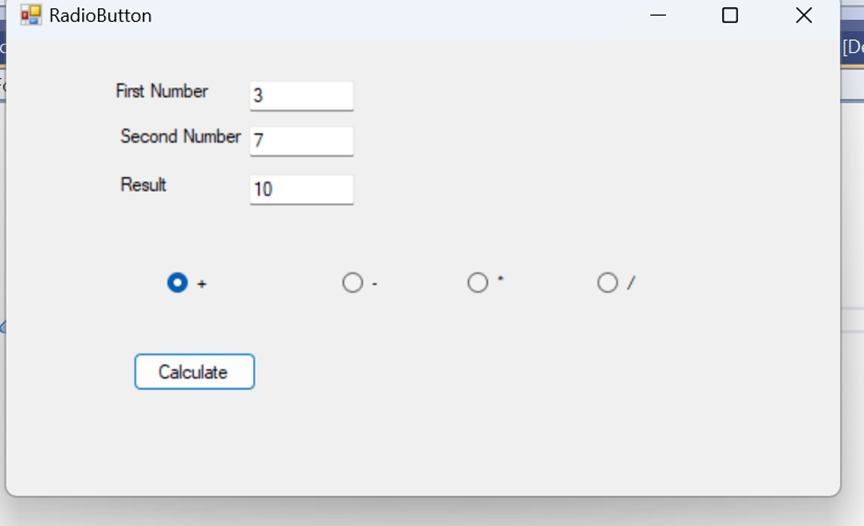
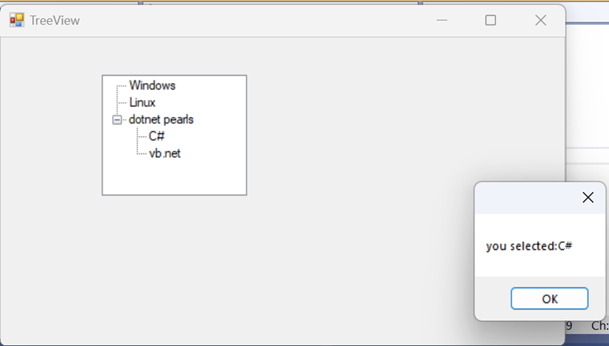


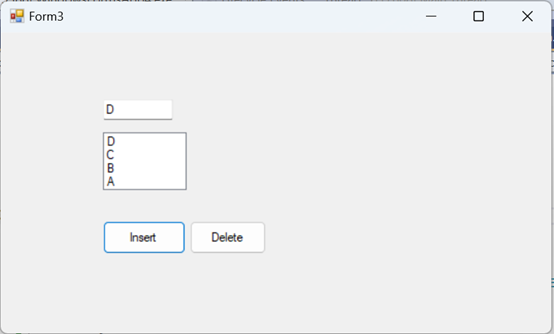
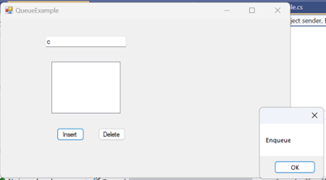



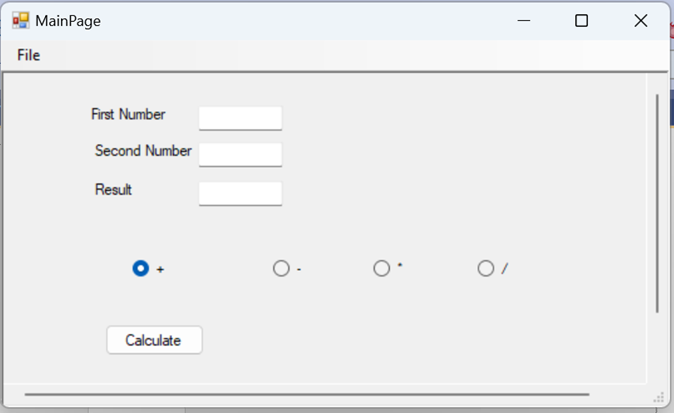







No comments:
Post a Comment